Hepatocytes
Hepatocytes are the chief functional cells of the liver and are responsible for the selective uptake, metabolism and excretion of most drugs.
Primary Human Hepatocytes
Primary human hepatocytes are the current model of choice for obtaining preclinical data and are regularly used by various pharmaceutical companies for safety assessment and DMPK filing with the FDA.
On conventional platforms (2D, sandwich culture), primary hepatocytes lose viability and function over time. Invitrocue’s 3D tri-culture model with stellate cells and kupffer cells has been shown to promote long-term maintenance of hepatocyte functionality, offering a better model to predict in vivo human outcomes.
Advantages of 3D hepatocyte culture compared with conventional 2D culture:
- High throughput and cost effective (seeding density of primary hepatocytes in 3D culture is 5-fold lower than in 2D culture)
- Long-term maintenance of liver-specific functions
- Improvement of liver CYP enzyme expression through co-culture with other liver cells
- Drug responses are closer to clinical outcomes

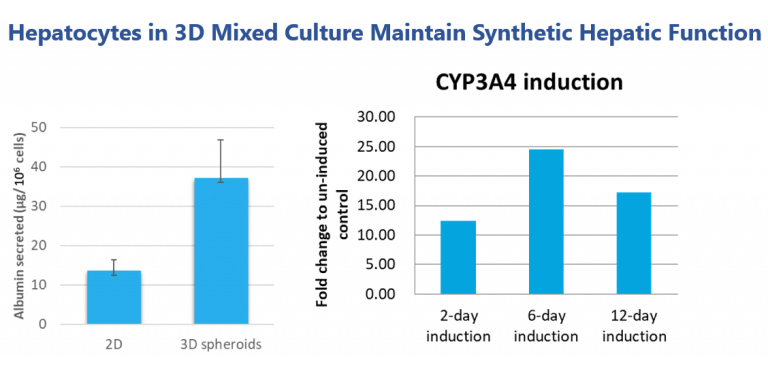
Hepatocytes in our 3D spheroid culture show better expression of hepatic functions in terms of albumin secretion. 3D hepatocyte spheroids are able to maintain liver cytochrome P450 enzyme functions and can be used for drug induction studies.
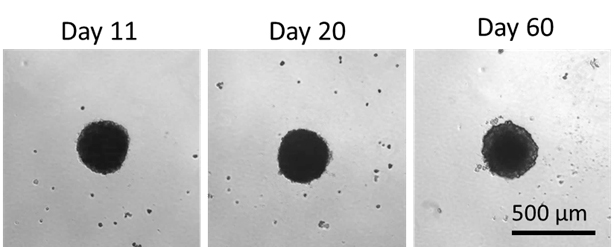
Hepatocyte viability can be maintained for 60 days, making it a good model for long-term drug toxicity studies.
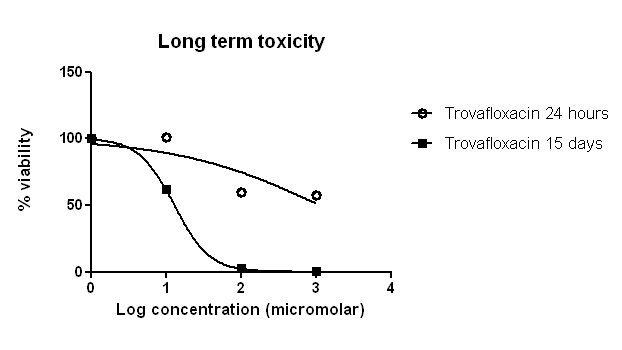
Trovafloxacin has been withdrawn from the market due to the risk of hepatotoxicity. Its hepatoxicity cannot be identified through conventional monoculture of hepatocytes. However, with our hepatocyte and kupffer cells co-culture model, we can replicate the microenvironment of the human liver and recapitulate immune-induced hepatotoxicity.
HBV Infection Model
Chronic Hepatitis B infection is prevalent in over two billion people worldwide and is responsible for 50% of hepatocellular carcinoma cases (www.hepb.org). Better in vitro or small animal models can improve the study of HBV and contribute to the development of new drugs against this disease.
At Invitrocue, we have established a 2D culture model for HBV infection using HepAD38 cells, a modified HepG2 cell line transfected with the HBV genome. Under the control of tetracycline, the viral expression is controlled by supressing pregenomic (pg) RNA synthesis. Upon removal of tetracycline from the culture medium, the expression of HBV transcript levels and viral particles is significantly up-regulated. Since the HepAD38 cell line can produce high levels of HBV DNA and viral expression is easily controlled, the HepAD38 assay has become a high-throughput and cost-effective model for new HBV drug testing.

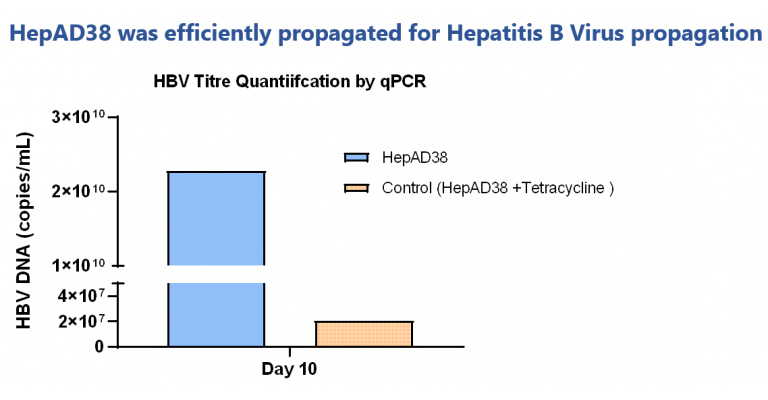
Quantification of precipitated virus showed good titre levels. Tetracycline control showed low virus titre.
Reference: Ladner, Stephanie K., et al. “Inducible expression of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) in stably transfected hepatoblastoma cells: a novel system for screening potential inhibitors of HBV replication.” Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 41.8 (1997): 1715-1720.
Co-Culture of Hepatocytes and iKCs
Kupffer cells (KC) constitute 80-90% of the residential macrophages present in the body and is the largest population of innate liver immune cells responsible for scavenger and phagocytic functions, as well as maintaining homeostasis of the liver.
Our hepatic co-cultures of iKCs and hepatocytes generated from the same iPSC donor results in a donor-matched co-culture model. This provides a powerful in vitro tool for modelling the liver and associated diseases such as NASH, Hepatitis Infection, as well as for evaluating immune-related drug induced liver injury (DILI).

Immune-induced DILI detected using Hepatocyte and KC Co-Culture System
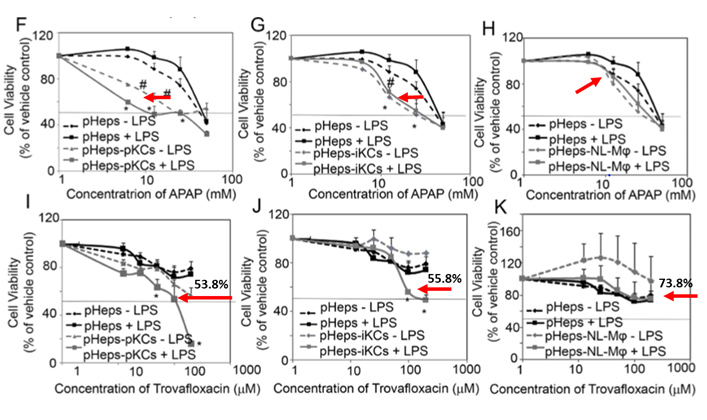
In the study above, reference drugs (acetaminophen (APAP) and Trovafloxacin) show a lower toxicity without immune cells. In the presence of immune cells, their hepatotoxicity dramatically increased (mimicking clinical response), an outcome that cannot be predicted using a conventional model.
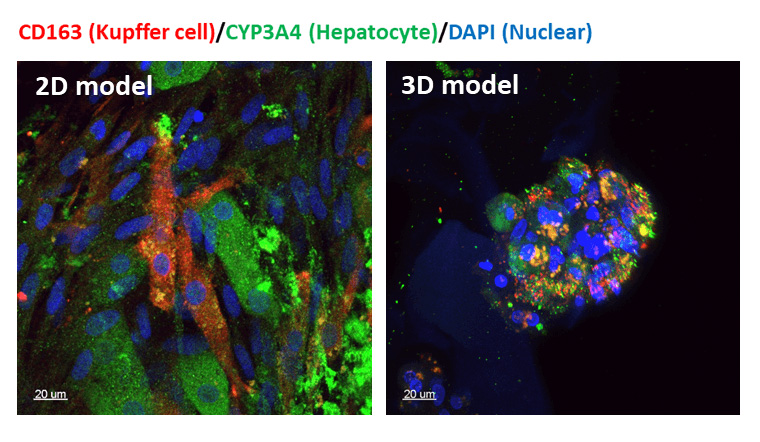
Confocal images of our hepatocyte-Kupffer co-culture, with Kupffer cells in red, Hepatocytes in green, and nucleus in blue.
3D Models require fewer cells, are more cost effective, and can be used for high-throughput drug screening.
